Folliculitis is a common condition caused by bacteria, fungi, or irritating substances. It usually enters the hair follicle, especially after shaving, friction, or hair transplantation. Other factors that can cause folliculitis include environmental irritants and contact with hair.
Treatment Methods for Folliculitis
Folliculitis treatment options vary depending on the etiology, severity, and distribution of the lesions. In uncomplicated superficial folliculitis cases, it can be treated with a simple antibacterial soap regimen and proper handwashing techniques. Oral antibiotics like metronidazole may be necessary for severe cases.
The disease is caused by various infectious organisms, including S. aureus, which commonly infect the skin. Many common antibiotics are ineffective against this organism, so a culture is required to select the appropriate antibiotic. Fungal folliculitis can occur on the body, face, and lower legs. The disease caused by viruses generally starts on the lips but can spread to hair and the scalp.
In general, the diagnosis of folliculitis is made based on appearance and symptoms. A culture of microbial pus in the pustules can help confirm the diagnosis. Hair affected by folliculitis can be examined with potassium hydroxide. In some cases, a small biopsy of the affected area may be required to determine whether it is a fungal or viral infection.
Folliculitis treatment may involve topical treatments available at a chemist or dermatologist. Folliculitis creams and antibiotics can be prescribed to alleviate symptoms and manage side effects. Sometimes the condition resolves on its own, but it’s important to seek immediate treatment if the infection persists. In most cases, folliculitis will self-resolve, but more severe cases may occasionally require antibiotic tablets.
As a treatment option for folliculitis, an antifungal shampoo or body wash should be used. Antifungal body washes contain ketoconazole, which is effective against fungal infections. For more severe cases, a doctor may prescribe a topical antifungal cream or tablet. Itching creams may also be prescribed for cases with significant itching.
In some cases, long-term antibiotic use for acne can lead to negative folliculitis. Over time, the bacteria causing acne become resistant to these drugs. In such cases, folliculitis can cause small white or red pimples accompanied by abscesses. Fortunately, folliculitis treatment usually resolves on its own, but if it lasts longer than expected, you should consult a dermatologist.
Symptomatic folliculitis can occur anywhere hair grows but typically appears in skin areas exposed to friction. Usually, a lump or rash is seen at the location where the disease occurs.
Causes of Folliculitis
There are two main types of folliculitis: eosinophilic and non-eosinophilic. Each type has its own symptoms and characteristics. In this article, we’ve discussed what can cause folliculitis, and hopefully, it will help you understand.
Bacterial folliculitis is the most common type and is caused by bacteria naturally present on the skin. Infection can occur through any form of skin irritation, such as cuts, scratches, or hair transplantation. In a mild case, the infection can be treated with topical antibiotics, but more severe cases may require antibiotics. Your doctor can take a sample of the pus to test for the presence of bacteria. Consult your doctor for treatment, as the disease may otherwise recur.
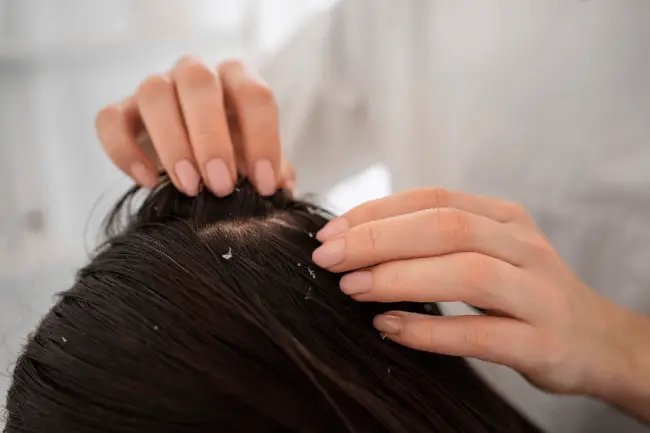

Applying a warm compress to the affected area can help people with folliculitis. Ideally, you should apply a warm compress three to four times a day and leave it on the skin for at least 15 minutes each time. For more severe cases, you may need to use a warm compress more frequently and refrain from shaving for at least 30 days. The heat from the compress can also aid in wound healing.
Symptoms of Folliculitis
Folliculitis is a common skin condition where hair follicles become inflamed. It does not affect hairless skin areas. In some cases, it can be quite uncomfortable. The disease typically presents as scaly, pus-filled blisters. The affected area may be irritated and painful.
To determine if the disease is present, you should examine the affected area. It should be clean and dry, and irritated skin should be treated. If symptoms persist, medical treatment may be necessary. The disease is not contagious but can spread from one part of the body to another. To prevent further infection, you should clean the affected area thoroughly with warm water and soap twice daily. Additionally, avoid using shared towels and bedding as they may harbor bacteria.